|
|
1. 概念
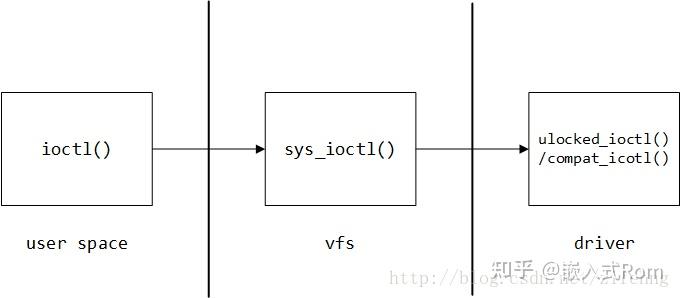
ioctl 是设备驱动程序中设备控制接口函数,一个字符设备驱动通常会实现设备打开、关闭、读、写等功能,在一些需要细分的情境下,如果需要扩展新的功能,通常以增设 ioctl() 命令的方式实现。
在文件 I/O 中,ioctl 扮演着重要角色,本文将以驱动开发为侧重点,从用户空间到内核空间纵向分析 ioctl 函数。
图片来源于网络
2. 用户空间 ioctl
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
int ioctl(int fd, int cmd, ...) ;
ioctl() 函数执行成功时返回 0,失败则返回 -1 并设置全局变量 errorno 值,如下:
EBADF d is not a valid descriptor.
EFAULT argp references an inaccessible memory area.
EINVAL Request or argp is not valid.
ENOTTY d is not associated with a character special device.
ENOTTY The specified request does not apply to the kind of object that the descriptor d references.
因此,在用户空间使用 ioctl 时,可以做如下的出错判断以及处理:
int ret;
ret = ioctl(fd, MYCMD);
if (ret == -1) {
printf(&#34;ioctl: %s\n&#34;, strerror(errno));
}
在实际应用中,ioctl 最常见的 errorno 值为 ENOTTY(error not a typewriter),顾名思义,即第一个参数 fd 指向的不是一个字符设备,不支持 ioctl 操作,这时候应该检查前面的 open 函数是否出错或者设备路径是否正确
3. 驱动程序 ioctl
long (*unlocked_ioctl) (struct file *, unsigned int, unsigned long);
long (*compat_ioctl) (struct file *, unsigned int, unsigned long);在新版内核中, 与 取代了 。unlocked_ioctl,顾名思义,应该在无大内核锁(BKL)的情况下调用;compat_ioctl,compat 全称 compatible(兼容的),主要目的是为 64 位系统提供 32 位 ioctl 的兼容方法,也是在无大内核锁的情况下调用。
在《Linux Kernel Development》中对两种 ioctl 方法有详细的解说。
在字符设备驱动开发中,一般情况下只要实现 unlocked_ioctl 函数即可,因为在 vfs 层的代码是直接调用 unlocked_ioctl 函数
// fs/ioctl.c
static long vfs_ioctl(struct file *filp, unsigned int cmd,
unsigned long arg)
{
int error = -ENOTTY;
if (!filp->f_op || !filp->f_op->unlocked_ioctl)
goto out;
error = filp->f_op->unlocked_ioctl(filp, cmd, arg);
if (error == -ENOIOCTLCMD) {
error = -ENOTTY;
}
out:
return error;
}
4. ioctl 用户与驱动之间的协议
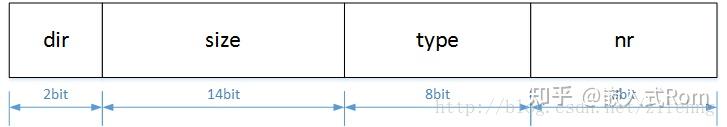
前文提到 ioctl 方法第二个参数 cmd 为用户与驱动的 “协议”,理论上可以为任意 int 型数据,可以为 0、1、2、3……,但是为了确保该 “协议” 的唯一性,ioctl 命令应该使用更科学严谨的方法赋值,在linux中,提供了一种 ioctl 命令的统一格式,将 32 位 int 型数据划分为四个位段,如下图所示:
在内核中,提供了宏接口以生成上述格式的 ioctl 命令:
// include/uapi/asm-generic/ioctl.h
#define _IOC(dir,type,nr,size) \
(((dir) << _IOC_DIRSHIFT) | \
((type) << _IOC_TYPESHIFT) | \
((nr) << _IOC_NRSHIFT) | \
((size) << _IOC_SIZESHIFT))
1.dir(direction),ioctl 命令访问模式(数据传输方向),占据 2 bit,可以为 _IOC_NONE、_IOC_READ、_IOC_WRITE、_IOC_READ | _IOC_WRITE,分别指示了四种访问模式:无数据、读数据、写数据、读写数据;
2.type(device type),设备类型,占据 8 bit,在一些文献中翻译为 “幻数” 或者 “魔数”,可以为任意 char 型字符,例如‘a’、’b’、’c’ 等等,其主要作用是使 ioctl 命令有唯一的设备标识;
3.nr(number),命令编号/序数,占据 8 bit,可以为任意 unsigned char 型数据,取值范围 0~255,如果定义了多个 ioctl 命令,通常从 0 开始编号递增;
4.size,涉及到 ioctl 函数 第三个参数 arg ,占据 13bit 或者 14bit(体系相关,arm 架构一般为 14 位),指定了 arg 的数据类型及长度,如果在驱动的 ioctl 实现中不检查,通常可以忽略该参数;
通常而言,为了方便会使用宏 _IOC() 衍生的接口来直接定义 ioctl 命令:
// include/uapi/asm-generic/ioctl.h
/* used to create numbers */
#define _IO(type,nr) _IOC(_IOC_NONE,(type),(nr),0)
#define _IOR(type,nr,size) _IOC(_IOC_READ,(type),(nr),(_IOC_TYPECHECK(size)))
#define _IOW(type,nr,size) _IOC(_IOC_WRITE,(type),(nr),(_IOC_TYPECHECK(size)))
#define _IOWR(type,nr,size) _IOC(_IOC_READ|_IOC_WRITE,(type),(nr),(_IOC_TYPECHECK(size)))
_IO: 定义不带参数的 ioctl 命令
_IOW: 定义带写参数的 ioctl 命令(copy_from_user)
_IOR: 定义带读参数的ioctl命令(copy_to_user)
_IOWR: 定义带读写参数的 ioctl 命令同时,内核还提供了反向解析 ioctl 命令的宏接口:
// include/uapi/asm-generic/ioctl.h
/* used to decode ioctl numbers */
#define _IOC_DIR(nr) (((nr) >> _IOC_DIRSHIFT) & _IOC_DIRMASK)
#define _IOC_TYPE(nr) (((nr) >> _IOC_TYPESHIFT) & _IOC_TYPEMASK)
#define _IOC_NR(nr) (((nr) >> _IOC_NRSHIFT) & _IOC_NRMASK)
#define _IOC_SIZE(nr) (((nr) >> _IOC_SIZESHIFT) & _IOC_SIZEMASK)
<hr/>
 |
|